40 indexing using labels in dataframe
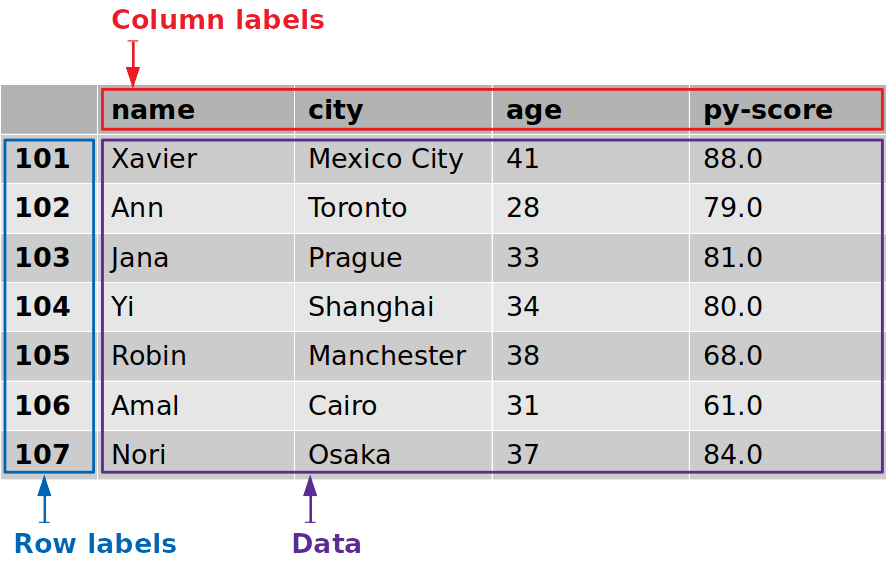
pandas.DataFrame — pandas 1.5.1 documentation The column labels of the DataFrame. dtypes. Return the dtypes in the DataFrame. empty. Indicator whether Series/DataFrame is empty. flags. Get the properties associated with this pandas object. iat. Access a single value for a row/column pair by integer position. iloc. Purely integer-location based indexing for selection by position. index. The index (row labels) of the … Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.5.1 documentation Indexing and selecting data# The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment. Allows intuitive getting and setting of subsets of the data set.
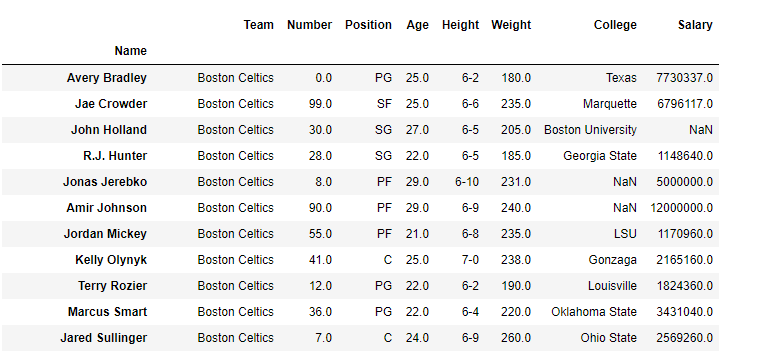
Python | Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Jan 10, 2019 · Indexing a DataFrame using .loc[ ]: This function selects data by the label of the rows and columns. The df.loc indexer selects data in a different way than just the indexing operator. It can select subsets of rows or columns. It can also simultaneously select subsets of rows and columns. Selecting a single row

Indexing using labels in dataframe
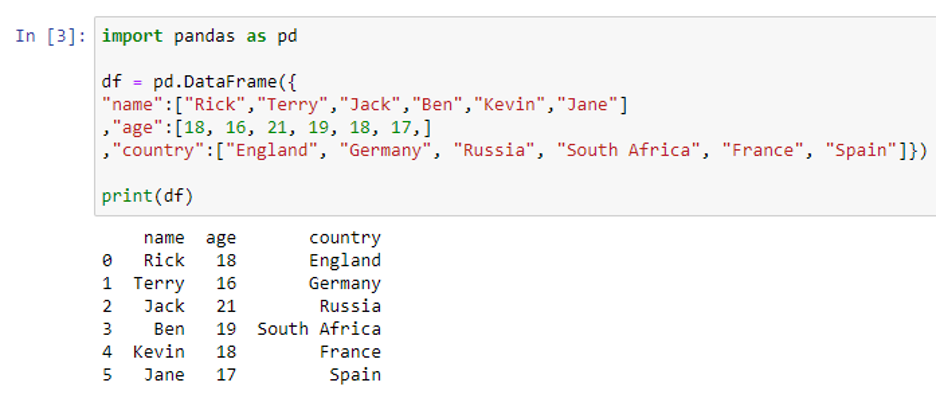
Using Pandas and Python to Explore Your Dataset Using the Indexing Operator If you think of a DataFrame as a dictionary whose values are Series , then it makes sense that you can access its columns with the indexing operator: >>> city_data [ "revenue" ] Amsterdam 4200 Tokyo 6500 Toronto 8000 Name: revenue, dtype: int64 >>> type ( city_data [ "revenue" ]) pandas.core.series.Series Intro to data structures — pandas 1.5.1 documentation The fundamental behavior about data types, indexing, axis labeling, and alignment apply across all of the objects. To get started, import NumPy and load pandas into your namespace: In [1]: import numpy as np In [2]: import pandas as pd. Fundamentally, data alignment is intrinsic. The link between labels and data will not be broken unless done so explicitly by you. We’ll give a … DataFrame — PySpark 3.3.1 documentation - Apache Spark Indexing, iteration¶ DataFrame.at ... Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns. DataFrame.swapaxes (i, j[, copy]) Interchange axes and swap values axes appropriately. DataFrame.swaplevel ([i, j, axis]) Swap levels i and j in a MultiIndex on a particular axis. DataFrame.take (indices[, axis]) Return the elements in the given positional indices along …
Indexing using labels in dataframe. Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.5.1 documentation Indexing and selecting data# The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment. Allows intuitive getting and setting of subsets of the data set. MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.5.1 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ... MultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.5.1 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ... pandas.Series — pandas 1.5.1 documentation One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels (including time series). Labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object supports both integer- and label-based indexing and provides a host of methods for performing operations involving the index. Statistical methods from ndarray have been overridden to automatically exclude missing data (currently represented as NaN). …
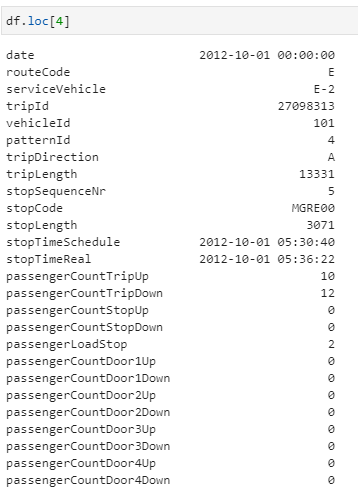
pandas.DataFrame.loc — pandas 1.5.1 documentation pandas.DataFrame.loc# property DataFrame. loc [source] # Access a group of rows and columns by label(s) or a boolean array..loc[] is primarily label based, but may also be used with a boolean array. Allowed inputs are: A single label, e.g. 5 or 'a', (note that 5 is interpreted as a label of the index, and never as an integer position along the ... DataFrame — PySpark 3.3.1 documentation - Apache Spark Indexing, iteration¶ DataFrame.at ... Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns. DataFrame.swapaxes (i, j[, copy]) Interchange axes and swap values axes appropriately. DataFrame.swaplevel ([i, j, axis]) Swap levels i and j in a MultiIndex on a particular axis. DataFrame.take (indices[, axis]) Return the elements in the given positional indices along … Intro to data structures — pandas 1.5.1 documentation The fundamental behavior about data types, indexing, axis labeling, and alignment apply across all of the objects. To get started, import NumPy and load pandas into your namespace: In [1]: import numpy as np In [2]: import pandas as pd. Fundamentally, data alignment is intrinsic. The link between labels and data will not be broken unless done so explicitly by you. We’ll give a … Using Pandas and Python to Explore Your Dataset Using the Indexing Operator If you think of a DataFrame as a dictionary whose values are Series , then it makes sense that you can access its columns with the indexing operator: >>> city_data [ "revenue" ] Amsterdam 4200 Tokyo 6500 Toronto 8000 Name: revenue, dtype: int64 >>> type ( city_data [ "revenue" ]) pandas.core.series.Series

























Post a Comment for "40 indexing using labels in dataframe"